general Microscopic Anatomy Biology Diagrams
general Microscopic Anatomy Biology Diagrams Microscopic anatomy (micro; small) is a branch of anatomy that relies on the use of microscopes to examine the smallest structures of the body; tissues, cells, and molecules. The extent to which microscopic anatomy can be examined is limited by the equipment available. Through a simple dissecting microscope, tissues can be viewed, organized and

The human body has four main categories of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular and neural tissues. The branch of biology that studies the microscopic structure of tissues is called histology. Compact bone, x.s. 400x Learning Outcomes. List the 4 main types and characteristics of tissue found in the human body
Human Anatomy and Physiology ... Biology Diagrams
The virtual slide box contains 275 microscope slides for the learning histology. Microscopic anatomy is studied by the use of microscopes. It is divided into two categories cytology and histology. Cytology is the microscopic study of cells of the human body and histology is the microscopic study of tissues of the human body. For a medical student, Microscopic anatomy is one of the most important concepts to learn and

While gross anatomy focuses on what we can see with our eyes, microscopic anatomy examines the structures at the cellular and tissue levels. It's akin to diving into a microscopic world, where the details become incredibly intricate. Visit Museums: Many science museums have exhibits on human anatomy. Watching a real body exhibit can be a

What Are the Main Subdivisions of Human Anatomy? Biology Diagrams
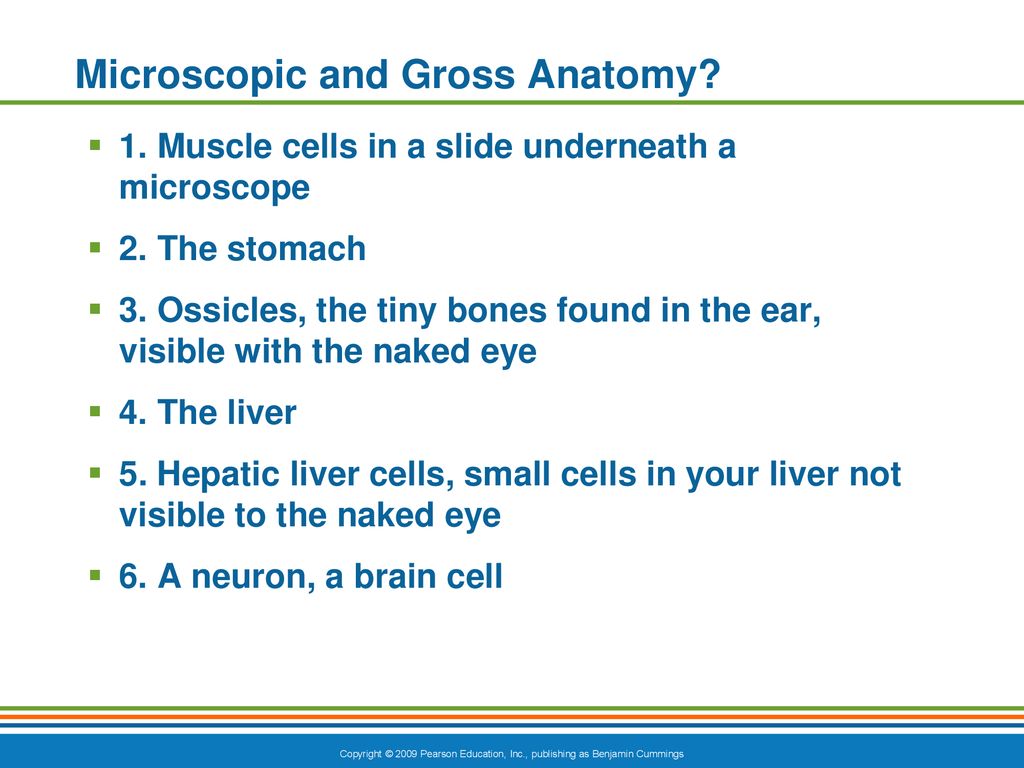
Human anatomy (gr. ἀνατομία, "dissection", from ἀνά, "up", and τέμνειν, "cut") is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. [1] Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. [1] Gross anatomy (also called macroscopic anatomy, topographical anatomy, regional anatomy, or anthropotomy) is the study of anatomical structures that can

Human ovum 120 um Most cells 10-30 um Red blood cell (RBC) 7 um Mitochondium 0.4-1.0 um Cilium 0.3 um Microvillus 100 nm Electron Micro-scope Microtubule 24 nm Myosin filaments 15 nm Intermediate fila-ments 10 nm Plasma mem-brane 9 nm Microfilaments (actin) 5 nm There are several challenges in learning histol-ogy. The first being that the view Explore the diverse branches of anatomy, including gross, microscopic, developmental, and functional, to understand the human body's structure and function. BiologyInsights Team Published Jul 21, 2024
